Stripe report finds the subscription economy is growing despite headwinds

Midjourney prompt: /imagine Carousel of credit cards, recurring lines to show passage of time, isometric, depth of field, --ar 16:9
- Recurring payment volume processed on Stripe is growing 16% faster than one-time payment volume, and subscription businesses are continuing to expand internationally.
- A majority of subscription businesses are turning toward flexible pricing strategies that include usage-based models and premium plans.
- One-third of businesses that report an increase in involuntary churn are not yet using third-party tools to reduce it.
SAN FRANCISCO AND DUBLIN—Stripe, a financial infrastructure platform for businesses, today published its State of Subscription and Billing Management report, analyzing how the leaders of 1,500 subscription companies are thinking about their strategy for the next 12 months. Businesses surveyed range from B2B SaaS companies and digital service providers to those offering physical product subscriptions.
Subscription businesses boomed during the COVID-19 pandemic as demand from consumers and businesses surged. And while pandemic-fueled growth has faded, subscription models continue to outperform the broader online economy: recurring payment volumes processed on Stripe are growing 16% faster than one-time payments.
Despite this growth, leaders of subscription companies are preparing for a more complex environment. Forty-three percent of business leaders who participated in the survey expect churn to increase as their customers cut back in response to volatility in the global economy. At the same time, 81% agree that the predictability of recurring revenue is more important than ever, and they are looking for additional ways to retain their existing customers.
Subscription business leaders are navigating this complex environment with three main approaches: pricing optimization, continued international expansion, and the use of automatic tools to reduce involuntary churn.
Optimizing pricing
With high inflation, price cuts are not an option for most subscription services, as their own costs are also increasing. Only 25% of business leaders say they are responding to customer churn by lowering prices. Instead, 40% plan to invest in new pricing strategies to better meet customers’ expectations and demonstrate the value of their services.
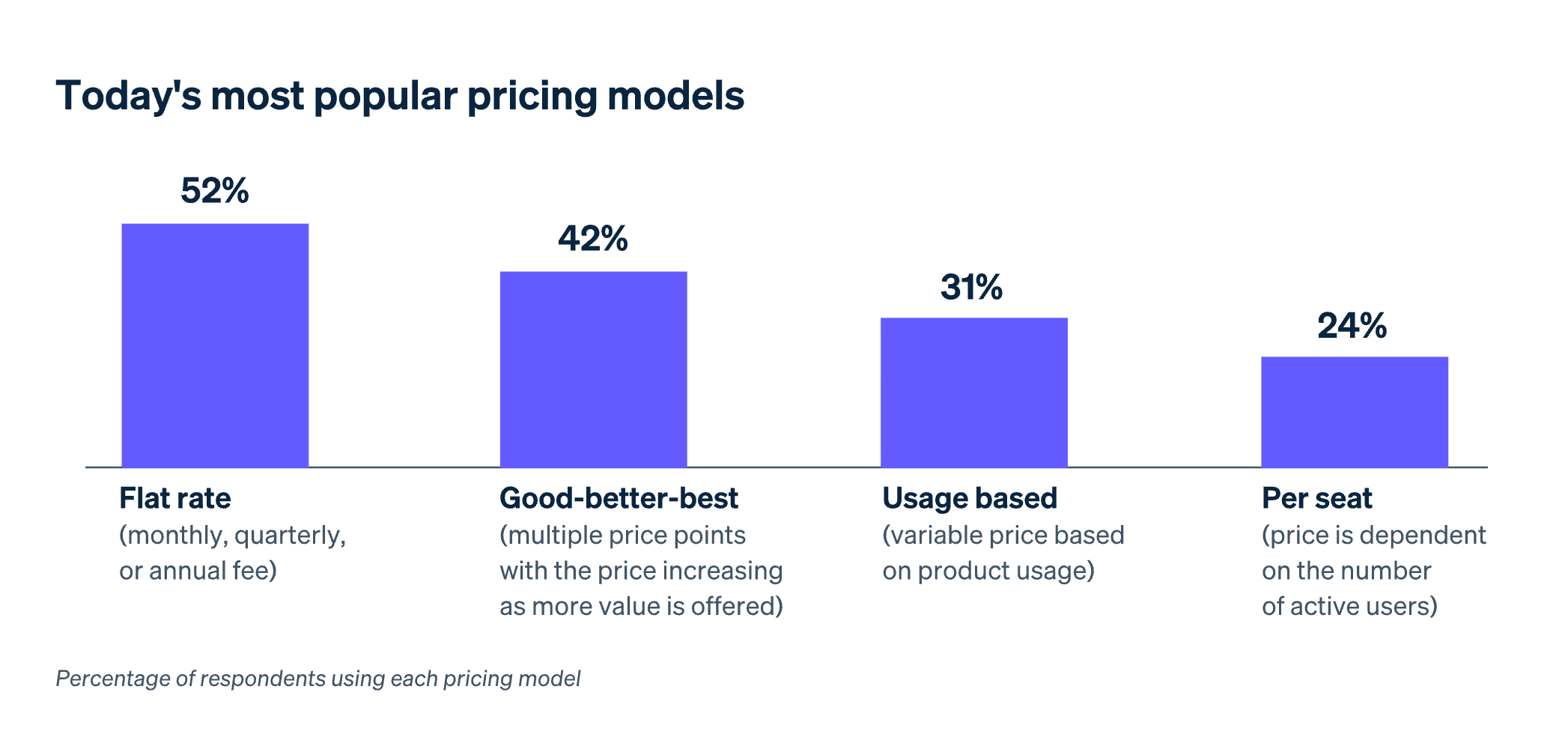
While flat-rate pricing remains the most common pricing model, macroeconomic uncertainty calls for a more flexible approach. Sixty-seven percent of respondents expect usage-based pricing to be more widely adopted, driven by price-sensitive subscribers. At the same time, subscription businesses are creating higher-tier premium options for less price-sensitive customers: 52% of financial services subscription firms and 42% of tech subscription companies surveyed plan to offer higher-priced premium plans.
“Combining tiered subscription pricing with usage-based top-ups allows us to scale our product to more people than a one-size-fits-all approach would have,” said Midjourney CFO Nadia Ali. “Stripe allows us to cater to customers with different interests and uses for our tools. By building more bespoke subscription plans with Stripe, we’re able to reach a wider customer group—from AI enthusiasts to those who are just starting out.”
Free trials are easy to implement and allow businesses to experiment with pricing optimization, but they present challenges of their own. Managing payments and trial cancellations is often costly and burdensome, as subscribers forget to cancel their subscription before their trial ends, resulting in support tickets and requests for refunds. SaaS startup Tango solved this by offering free trials that don’t require a payment method, letting subscribers experience the product’s value without incurring the risk of managing refund support.
Expanding internationally
As pandemic-era hypergrowth has faded, subscription businesses are looking abroad to continue adding customers. International scalability is a key advantage of many subscription services, as they often don’t require physical logistics.
More than half of respondents are planning an international expansion within the next 12 months. In doing so, businesses understand that payment habits vary across the world, and that customers in different localities expect to be able to pay with their preferred methods. Given that, 71% of respondents said they are looking to add at least one new payment method over the next year.
Reducing involuntary churn
At the same time subscription businesses are looking for new customers abroad, they are investing in tools to retain their existing ones—especially tools that prevent involuntary churn, which occurs when a breakdown in payment information causes a subscription to lapse unintentionally. Forty-one percent of businesses surveyed reported an increase in involuntary churn, yet one-third (32%) of these are still not taking advantage of tools which can automatically help reduce the chance of it happening.
These tools include Stripe’s smart retries, which uses machine learning algorithms to determine the best time to retry failed payment attempts, and card account updater, which automatically replaces expired cards with new payment details. Revenue recovery tools significantly drive down involuntary churn, reduce lost revenue, and maximize value from customer purchases and subscriptions. Stripe’s automated revenue recovery features earned Stripe users an additional $3.8 billion in revenue in 2022.
“Recurring revenue models exploded over the past few years along with the rest of the internet economy, and they’ve stuck around because they give businesses and consumers an easy way to get a predictable return on their investment,” said Emily Glassberg Sands, head of information at Stripe. “Business leaders are now kicking off the next chapter of the subscription economy, relying on third-party tools to expand to new markets, experiment with different pricing models, and make sure they’re earning more revenue from their loyal customers.”
The State of Subscription and Billing Management report compiled survey responses from 1,500 founders, executives, and product, payments, and engineering leaders across Australia, France, Germany, Japan, Mexico, Singapore, the United Kingdom, and the United States.